The drastic measures taken in the UK to tackle coronavirus have been justified because of the need to save lives.
Modelling by Imperial College London – used to inform government – suggests 500,000 could die if we do nothing.
Even the government’s previous strategy to slow the spread was likely to lead to 250,000 deaths, the research showed.
The warnings prompted ministers to announce on Monday the most draconian crackdown on freedom in peacetime with the public told not to go to pubs, clubs or theatres, and to work from home if possible.
The move has hit the economy, putting jobs at risk and prompting schools to be closed and exams cancelled.
No other option – experts
Professor Neil Ferguson, one of the lead academics involved in the modelling, told the BBC’s Today Programme this week there was “no option” if 250,000 lives were not to be risked.
Sir Patrick Vallance, the government’s chief scientific adviser, said in an appearance before the Health Select Committee, that the hope was to keep the death toll below 20,000 by suppressing the virus.
That would still be worse than those killed by flu, he said, giving a number of 8,000 per year.
He said limiting deaths to 20,000 would be “horrible” but still represented a “good outcome” given where we are.


Would these people be dying anyway?
The figures for coronavirus are eye-watering. But what is not clear – because the modellers did not map this – is to what extent the deaths would have happened without coronavirus.
Of course, this will never truly be known until the pandemic is over, which is why modelling is very difficult and has to be heavily-caveated.
But given that the old and frail are the most vulnerable, would these people be dying anyway?
Every year more than 500,000 people die in England and Wales: factor in Scotland and Northern Ireland, and the figure tops 600,000.
The coronavirus deaths will not be on top of this. Many would be within this “normal” number of expected deaths. In short, they would have died anyway.
It was a point conceded by Sir Patrick at a press conference on Thursday when he said there would be “some overlap” between coronavirus deaths and expected deaths – he just did not know how much of an overlap.
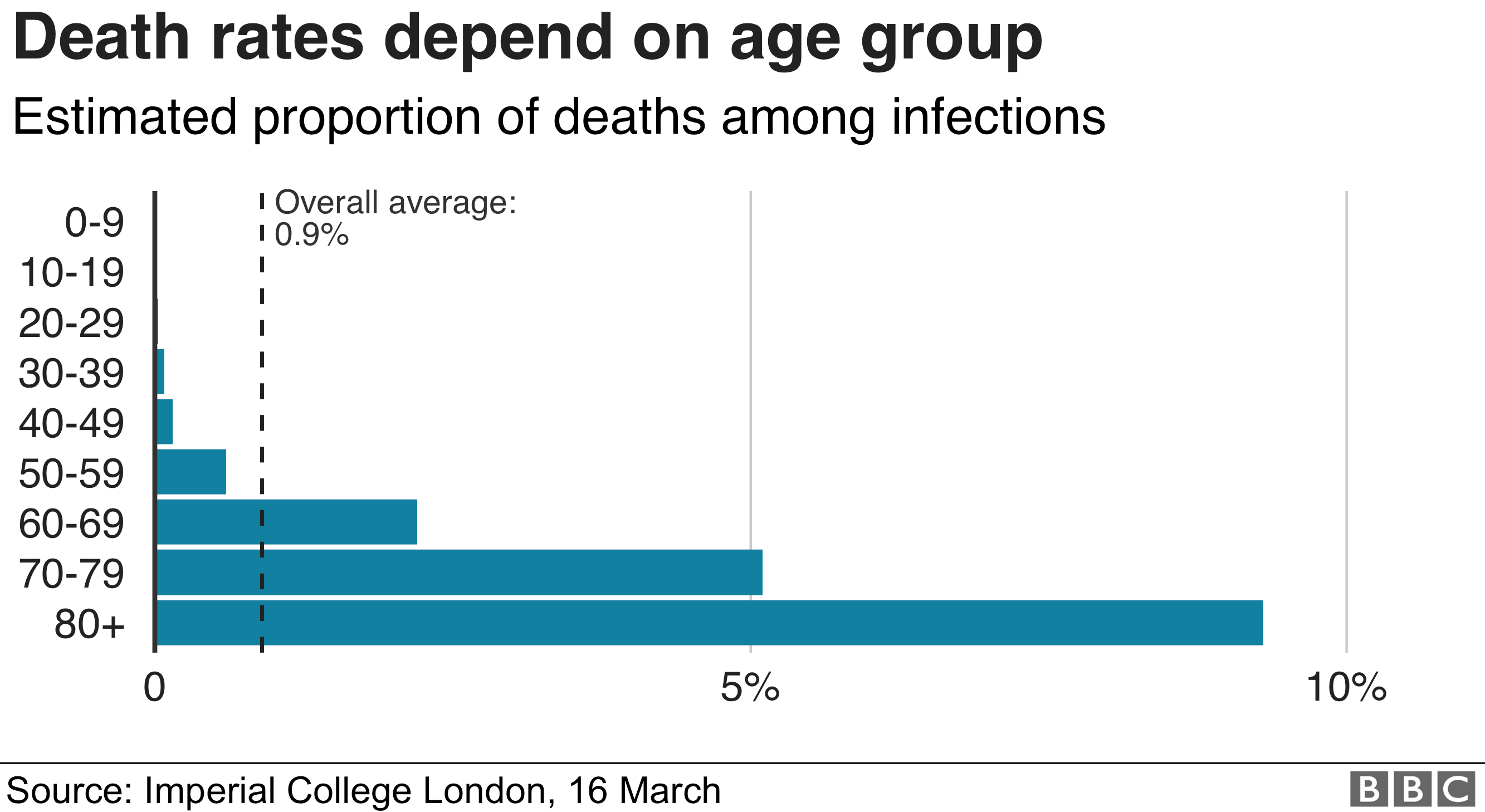

The flu comparison
In contrast, the figure he gave for flu deaths to MPs – 8,000 – is different. It is actually the number of deaths over and above what you would expect to happen in any given year.
Many more die with flu, but the figure gives you an indication of how many more die because of flu, whereas the 20,000, 250,000 and 500,000 figures for coronavirus are simply the number of deaths linked to coronavirus.
The testing which has been done in many countries means we know when a patient dies with the virus inside their body. What it does not tell us is to what extent coronavirus contributed to the death.
Why better intelligence is needed
 There are, of course, other factors at play here. Left unchecked, the deaths would come very quickly.
There are, of course, other factors at play here. Left unchecked, the deaths would come very quickly.The 500,000 deaths could all occur in the UK by August, the modellers said.
This in itself would overwhelm the health service – if they were right – putting even more lives at risk, because care would not be available for others.
But there is certainly evidence to suggest the modellers have underestimated the ability of the NHS to increase intensive care capacity.
NHS England chief executive Simon Stevens suggested intensive care capacity could be doubled, after this modelling came out.
There are 3,700 adult intensive care beds in England – and well over 4,000 if you include the rest of UK.
Eight in 10 are in use at any one point. Although you can reduce that by a quarter if you stop routine operations (as has been done).
Thousands more ventilators can be sourced from the private sector, old and new stocks, Ministry of Defence and from theatres that will no longer being carrying out operations.
Sir Simon suggested it could bring the total number of ventilators close to 12,000 – although there is some doubt whether that would translate to 12,000 intensive care beds given they would need staffing.
What else has not been done is a proper assessment of the economic and social costs of the measures taken, which themselves will put lives and health at risk.
As we get deeper into this crisis, we will need much greater intelligence on just how many lives are truly being saved, and compare that to the wider cost to society, so the government and the public can weigh up the best course of action.
The drastic measures taken in the UK to tackle coronavirus have been justified because of the need to save lives.
Modelling by Imperial College London – used to inform government – suggests 500,000 could die if we do nothing.
Even the government’s previous strategy to slow the spread was likely to lead to 250,000 deaths, the research showed.
The warnings prompted ministers to announce on Monday the most draconian crackdown on freedom in peacetime with the public told not to go to pubs, clubs or theatres, and to work from home if possible.
The move has hit the economy, putting jobs at risk and prompting schools to be closed and exams cancelled.
No other option – experts
Prof Neil Ferguson, one of the lead academics involved in the modelling, suggested on the BBC’s Today Programme this week there was “no option” if 250,000 lives were not to be risked.
Sir Patrick Vallance, the government’s chief scientific adviser, said in an appearance before the Health Select Committee, that the hope was to keep the death toll below 20,000 by suppressing the virus.
That would still be worse than those killed by flu, he said, giving a number of 8,000 per year.
He said limiting deaths to 20,000 would be “horrible” but still represented a “good outcome” given where we are.


Would these people be dying anyway?
The figures for coronavirus are eye-watering.
But what is not clear – because the modellers did not map this – is to what extent the deaths will happen without coronavirus.
Of course, this will never truly be known until the pandemic is over, which is why modelling is a very difficult and has to be heavily-caveated.
But given that the old and frail are the most vulnerable, would these people be dying anyway?
Every year more than 500,000 people die in England and Wales: factor in Scotland and Northern Ireland, and the figure tops 600,000.
The coronavirus deaths will not be on top of this. Many would be within this “normal” number of expected deaths. In short, they would have died anyway.
It was a point conceded by Sir Patrick at a press conference on Thursday when he said there would be “some overlap” between coronavirus deaths and expected deaths – he just did not know how much of an overlap.
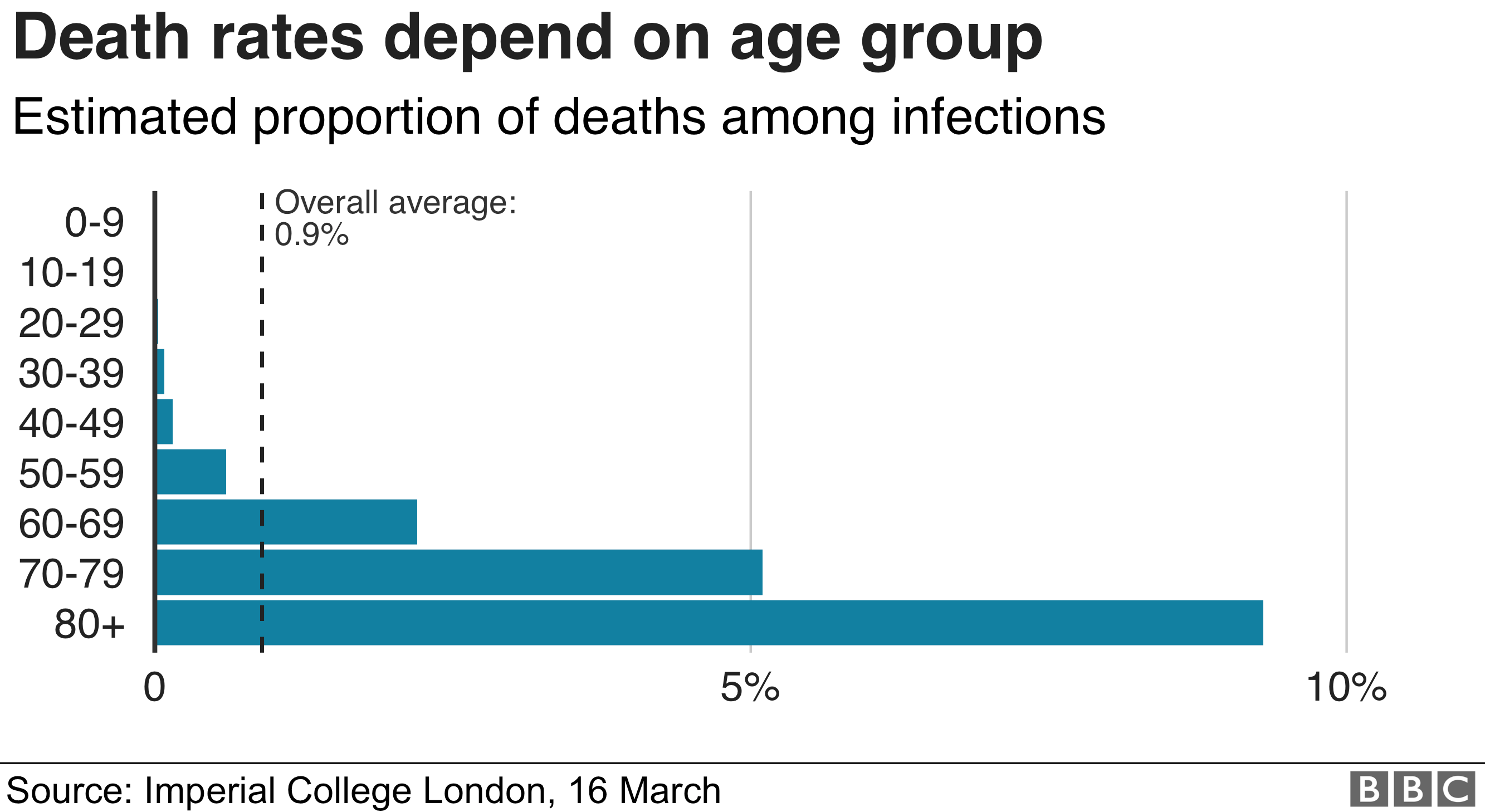

The flu comparison
In contrast, the figure he gave for flu deaths to MPs – 8,000 – is different. It is actually the number of deaths over and above what you would expect to happen in any given year.
Many more die with flu, but the figure gives you an indication of how many more die because of flu, whereas the 20,000, 250,000 and 500,000 figures for coronavirus are simply the number of deaths linked to coronavirus.
The testing which has been done in many countries means we know when a patient dies with the virus inside their body. What it does not tell us is to what extent coronavirus contributed to the death.
Why better intelligence is needed

There are, of course, other factors at play here. Left unchecked, the deaths would come very quickly.
The 500,000 deaths could all occur in the UK by August, the modellers said.
This in itself would overwhelm the health service – if they were right – putting even more lives at risk, because care would not be available for others.
But there is certainly evidence to suggest the modellers have underestimated the ability of the NHS to increase intensive care capacity.
NHS England chief executive Sir Simon Stevens suggested the number of available ventilators could be rapidly increased, after this modelling came out.
There are 3,700 adult intensive care beds in England – and well over 4,000 if you include the rest of UK.
Eight in 10 are in use at any one point. Although you can reduce that by a quarter if you stop routine operations (as has been done).
Thousands more ventilators can be sourced from the private sector, old and new stocks, Ministry of Defence and from theatres that will no longer being carrying out operations.
Sir Simon suggested it could bring the total number of ventilators close to 12,000 – although there is some doubt whether that would translate to 12,000 intensive care beds given they would need staffing.
What else has not been done is a proper assessment of the economic and social costs of the measures taken, which themselves will put lives and health at risk.
As we get deeper into this crisis, we will need much greater intelligence on just how many lives are truly being saved, and compare that to the wider cost to society, so the government and the public can weigh up the best course of action.
 Home Of Ghana News Ghana News, Entertainment And More
Home Of Ghana News Ghana News, Entertainment And More




